Pointer Arithmetic Void Pointer

But you can do it somehow.
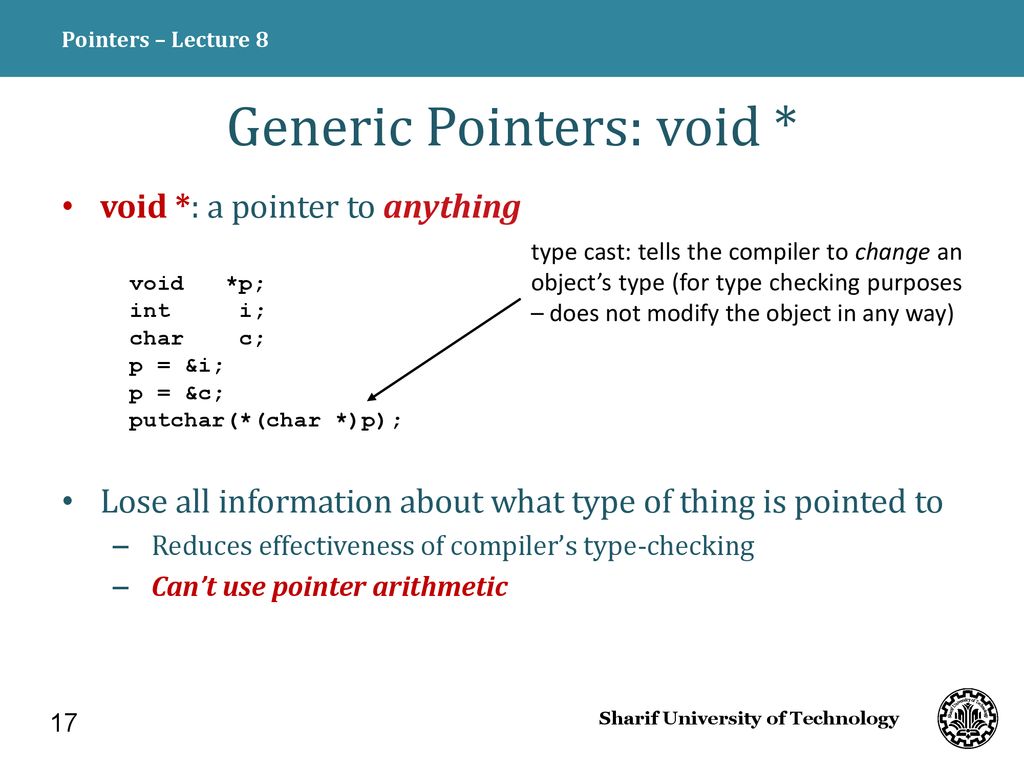
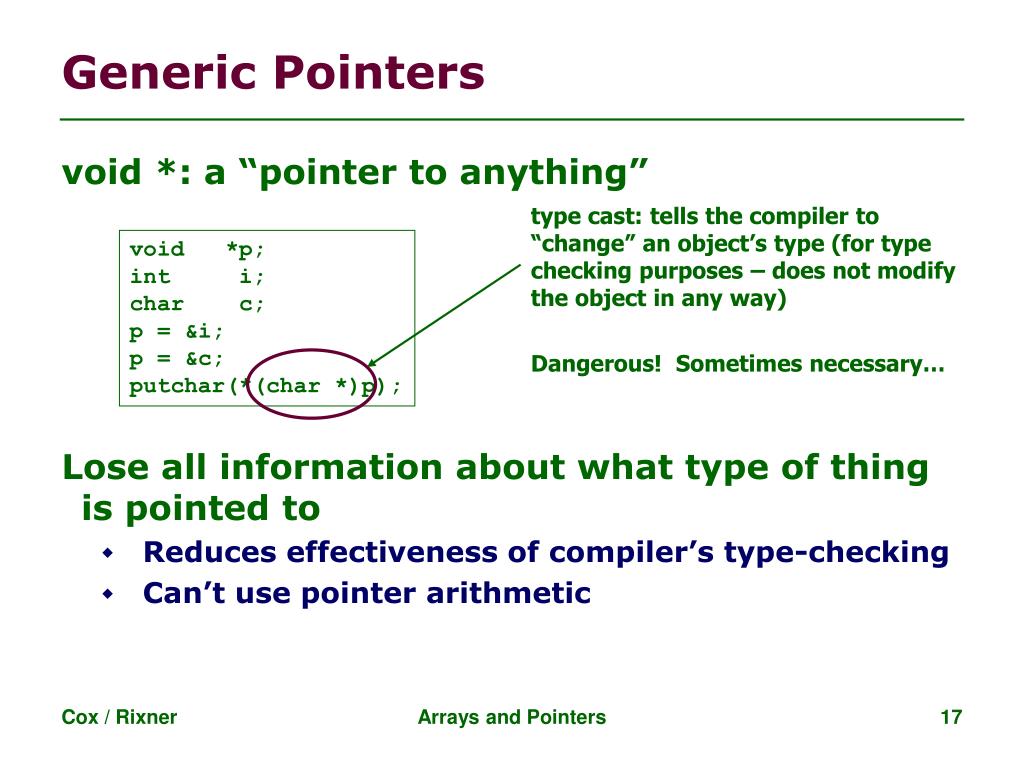
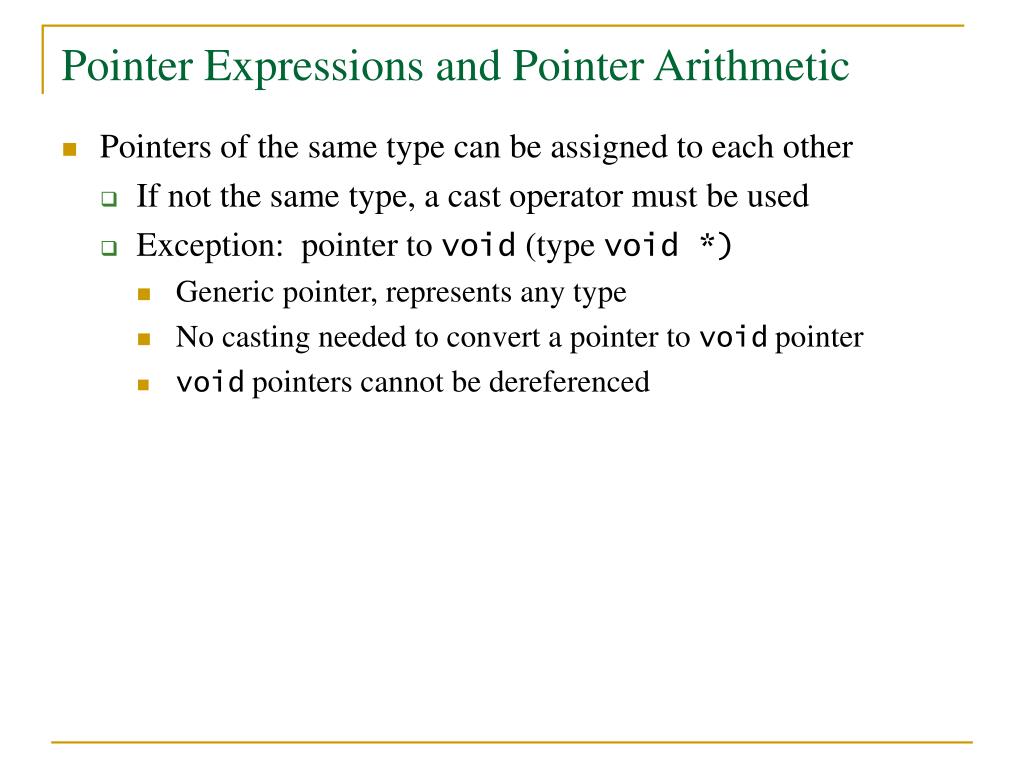
Pointer arithmetic void pointer. This is because pointer arithmetic requires the pointer to know what size object it is pointing to so it can increment or decrement the pointer appropriately it is pretty much a similar situation with dereferencing a void pointer. The pointer concept in c is very useful as it helps in memory allocation and address management. But they cannot be directly dereferenced. We need to apply the proper typecasting so that we can perform the arithmetic operations on the void pointers.
For example the following program compiles and runs fine in gcc. However some compiler supports void pointer arithmetic by assuming it as a char pointer. If you subtract p2 from p1 i e p1 p2 then the answer will be negative i e 4. Initialize a 7.
Referencing and dereferencing plays a vital role in pointer concept as well as in void pointer. To perform pointer arithmetic on void pointer you must first typecast to other type. The void pointers are more flexible as they can point to any type. However in gnu c it is allowed by considering the size of void is 1.
2 it can t be used as dereferenced. Pointer arithmetic in void pointers another important point i want to mention is about pointer arithmetic with void pointer. For dereferencing the void pointer needs to be converted to a pointer that points to a value with the concrete data type. 2 the c standard doesn t allow pointer arithmetic with void pointers.
It is not possible to do pointer arithmetic on a void pointer. Let s see the below example. We cannot apply the arithmetic operations on void pointers in c directly. You can t do it directly.
It helps in implementing two types of pointers namely void pointers and generic pointers. Example of void pointer arithmetic. Before you apply pointer arithmetic in void pointers make sure to provide a proper typecast first otherwise you may get unexcepted results. Pointer arithmetic between two pointers if we have two pointers p1 and p2 of base type pointer to int with addresses 1000 and 1016 respectively then p2 p1 will give 4 since the size of int type is 4 bytes.
We have shown the working of the null pointer void pointer in the following code example. Declare a pointer p as void. Void pointer arithmetic is illegal in c programming due to the absence of type. Algorithm begin declare a of the integer datatype.
1 pointer arithmetic is not possible with void pointer due to its concrete size. Consider the following example. Initialize p pointer to a. Therefore it is sometimes called a general purpose pointer.
Print integer variable is.